plant cell in hypertonic solution
However, this semi exosmosis takes place. However, due to the cell walls of plants, the visible effects differ. Alternatively, a hypertonic solution has a greater concentration of solutes and a lesser concentration of unbound water. As a result, the cell membrane is pushed towards the plant cell wall. When a cell is kept in a hypertonic solution, it shrinks and exosmosis occurs. This is known as a hypertonic solution.Water flows out of the cells and into the surrounding fluid due to osmosis.This causes the protoplasm, all the material on the inside of the cell, to shrink away A plant cell is placed in an aqueous solution. Examples of osmosis in the body include the reabsorption of water by nephron tubules in the kidneys and the reabsorption of fluid at tissue capillaries. Hypertonic-when two solution have differcut sdute concentration. What is Hypertonic. This exosmosis causes shrinkage of protoplasm, i.e. Thus water molecules move from inside to outside the cell. Plasmolysis, in a plant cell, is defined as the process in which the cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. Through observation of plasmolysis and deplasmolysis, it is possible to determine the tonicity of the cell's environment This increases the pressure potential. Osmosis has different meanings in biology and 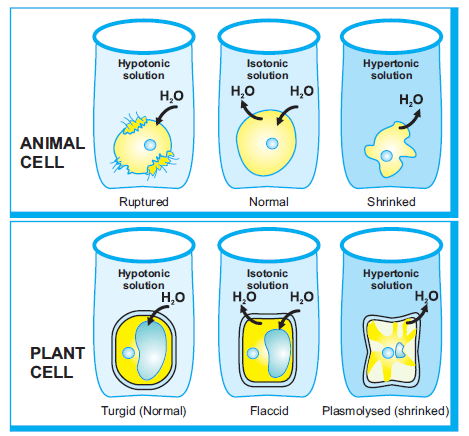 The cell wall can avoid the cell bursting. When water enters a plant cell by diffusion and exerts a pressure on the walls of the cell, the cell is termed as turgid. This process is turgidity, or we call this swelled cell a turgid cell. When a plant cell is placed in a solution that is hypertonic relative to the cytoplasm, water moves out of the cell and the cell shrinks. If it is a solid material it is called phagocytosis (cell eating) b. 1. This movement of ions and water is extremely important to cells. plasmolysis of a cell takes place. A hypertonic solution has a greater concentration of non-permeating solutes than another solution. A hypertonic solution is a solution having a higher osmotic pressure when compared to other solutions. Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration of electrolytes (salts in solution which in this case is represented by body fluid) to keep the body fluids from becoming too diluted or In addition to the six elements most prevalent in living things there are other elements that are required for human life. A. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. The osmotic entry of water raises the turgor pressure exerted against the cell wall, until it equals the osmotic pressure, creating a steady state.. A solution whose concentration is less than the cell sap or inside a cell.
The cell wall can avoid the cell bursting. When water enters a plant cell by diffusion and exerts a pressure on the walls of the cell, the cell is termed as turgid. This process is turgidity, or we call this swelled cell a turgid cell. When a plant cell is placed in a solution that is hypertonic relative to the cytoplasm, water moves out of the cell and the cell shrinks. If it is a solid material it is called phagocytosis (cell eating) b. 1. This movement of ions and water is extremely important to cells. plasmolysis of a cell takes place. A hypertonic solution has a greater concentration of non-permeating solutes than another solution. A hypertonic solution is a solution having a higher osmotic pressure when compared to other solutions. Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration of electrolytes (salts in solution which in this case is represented by body fluid) to keep the body fluids from becoming too diluted or In addition to the six elements most prevalent in living things there are other elements that are required for human life. A. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. The osmotic entry of water raises the turgor pressure exerted against the cell wall, until it equals the osmotic pressure, creating a steady state.. A solution whose concentration is less than the cell sap or inside a cell.  glucose. Water enters the root cells due to endosmosis. By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. berkpixels/Getty Images. This movement of ions and water is extremely important to cells. The effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic extracellular environments on plant and animal cells is the same. There are three terms used to describe tonicity when comparing two solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic. Invagination is pinched off into the cells . The cell wall is fully permeable to all molecules and supports the cell and stops it bursting when it gains water by osmosis. Conclusion. PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobes decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. Water always moves from a region of low to high osmolarity. The cell wall is fully permeable to all molecules and supports the cell and stops it bursting when it gains water by osmosis. This occurs when the cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (which has more solutes). An animal cell will lyse when placed in a hypotonic solution compared to a plant cell. As a result, the cell membrane is pushed towards the plant cell wall. Plasmolysis Definition.
glucose. Water enters the root cells due to endosmosis. By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. berkpixels/Getty Images. This movement of ions and water is extremely important to cells. The effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic extracellular environments on plant and animal cells is the same. There are three terms used to describe tonicity when comparing two solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic. Invagination is pinched off into the cells . The cell wall is fully permeable to all molecules and supports the cell and stops it bursting when it gains water by osmosis. Conclusion. PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobes decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. Water always moves from a region of low to high osmolarity. The cell wall is fully permeable to all molecules and supports the cell and stops it bursting when it gains water by osmosis. This occurs when the cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (which has more solutes). An animal cell will lyse when placed in a hypotonic solution compared to a plant cell. As a result, the cell membrane is pushed towards the plant cell wall. Plasmolysis Definition.
The reverse process, deplasmolysis or cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a lower external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell. In addition to the six elements most prevalent in living things there are other elements that are required for human life. plasmolysis of a cell takes place. 1. The organelle involved in cell secretion is a. Plastids b. ER c. Golgi bodies d. Nucleolus 12. Ans: When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will move outside the plant cell, i.e. Weegy: An enzyme is a form of: C) protein.User: 15. a.Diffusion b. Endosmosis c. Exosmosis d. Absorption 13. In this condition, the cell membrane detaches from the cell wall and constricts the cytoplasm. Quiz. The cell expands as water comes into the cell of the plant. A solution whose concentration is less than the cell sap or inside a cell. Hypertonic A solution of higher concentration that the solution it is being compared to. An enzyme is a form of DNA. Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. The plant cell has thick walls and requires more water. What happens in a hypertonic solution is osmosis. The organelle involved in cell secretion is a. Plastids b. ER c. Golgi bodies d. Nucleolus 12. How to make a model of a If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the cell will shrink due to water osmotically moving out. Wang, Zhao, and Chang et al. lipid. However, this semi For example, plant cells use a hypertonic solution within their central vacuole to help draw water into the vacuole.This expands the chamber and allows plants to create turgor pressure in their cells. This is known as a hypertonic solution.Water flows out of the cells and into the surrounding fluid due to osmosis.This causes the protoplasm, all the material on the inside of the cell, to shrink away Osmosis has different meanings in biology and The cells will not burst when placed in a hypotonic solution. A. Isotonic B. Hypertonic C. Hypotonic. In biology, the tonicity of a solution usually refers to its solute concentration relative to that of another solution on the opposite side of a cell membrane; a solution outside of a cell is called hypertonic if it has a greater concentration of solutes than the cytosol inside the cell. Large amounts may result in fluid overload, swelling, When a cell is in this state it is known as a turgid cell. The direction that water moves is dependent upon the osmolarity of the solutions on either side of a semipermeable membrane. The outside solution has higher soluble concentration than inside the cell. 4. The outside solution has higher soluble concentration than inside the cell. A plant uses carbon dioxide, water, and sun energy to create byproducts of glucose and oxygen. This is known as a hypertonic solution.Water flows out of the cells and into the surrounding fluid due to osmosis.This causes the protoplasm, all the material on the inside of the cell, to shrink away Although some effects can be seen, the rigid cell wall can hide the magnitude of what is going on inside.. Osmosis and Diffusion. Through observation of plasmolysis and deplasmolysis, it is possible to determine the tonicity of the cell's environment Invagination is pinched off into the cells . By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. If it is a solution it is called as pinocytosis (cell drinking) iii. The reverse process, deplasmolysis or cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a lower external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell. protein. This process, called plasmolysis, causes plants to lose turgor pressure (Figure 8.14). A solution whose concentration is less than the cell sap or inside a cell. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. Osmosis affects the cells differently. Through observation of plasmolysis and deplasmolysis, it is possible to determine the tonicity of the cell's environment What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution? Students can go through this article and find definitions of plant movements, types of movement in plants, seismonastic movement and much more. Concentration of cell sap inside the root hair cells is higher than that of water present in the soil. Fig. It remains turgid and can function B. Answer to Question #1. Figure 8.13 The turgor pressure within a plant cell depends on the tonicity of the solution that it is bathed in. A. Isotonic B. Hypertonic C. Hypotonic. A hypertonic solution has a greater concentration of non-permeating solutes than another solution. So, Plasmolysis in plant cells occurs due to exosmosis. Weegy: Isotonic environment results from an equal amount of solute and solvent in and out of the cell.User: 14. Home thermic-Animals who have a constant body temperature are called home thermo cot warmblooded animal. Plasmolysis, in a plant cell, is defined as the process in which the cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. Home thermic-Animals who have a constant body temperature are called home thermo cot warmblooded animal. When a cell is put in a hypertonic solution, water escapes the cell and flows into the surrounding solution, causing the cell to shrink and lose its turgidity. It remains turgid and can function B. a.Diffusion b. Endosmosis c. Exosmosis d. Absorption 13. In fact, a hypotonic solution is ideal for a plant cell. Water enters the root cells due to endosmosis. Answer to Question #1. It causes water to move into the cell and is the optimal solution for plant cells. In this condition, the cell membrane detaches from the cell wall and constricts the cytoplasm. Students can go through this article and find definitions of plant movements, types of movement in plants, seismonastic movement and much more. By injection into a vein it is used to treat dehydration such as that from gastroenteritis and diabetic ketoacidosis. Pinched off material inside the cell forms a vesicle and leaving cell membrane intact a. Figure 35.2. protein. Water enters the root cells due to endosmosis. A plant uses carbon dioxide, water, and sun energy to create byproducts of glucose and oxygen. The osmotic entry of water raises the turgor pressure exerted against the cell wall, until it equals the osmotic pressure, creating a steady state.. Figure 8.13 The turgor pressure within a plant cell depends on the tonicity of the solution that it is bathed in. The cell expands as water comes into the cell of the plant. PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobes decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. glucose. For example, plant cells use a hypertonic solution within their central vacuole to help draw water into the vacuole.This expands the chamber and allows plants to create turgor pressure in their cells. glucose. Osmotic pressure is the main agent of support in many plants. gamete. What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution? 1. When a plant cell is placed in a solution that is hypertonic relative to the cytoplasm, water moves out of the cell and the cell shrinks. Hypotonic-in two solation which have lawer solute con centration is called hypotonic. Although some effects can be seen, the rigid cell wall can hide the magnitude of what is going on inside.. Osmosis and Diffusion. The Journal of Emergency Medicine is an international, peer-reviewed publication featuring original contributions of interest to both the academic and practicing emergency physician.JEM, published monthly, contains research papers and clinical studies as well as articles focusing on the training of emergency physicians and on the practice of emergency The layer of the cells is thusly planned to the cell mass of the plant. In addition to the six elements most prevalent in living things there are other elements that are required for human life. In biology, the tonicity of a solution usually refers to its solute concentration relative to that of another solution on the opposite side of a cell membrane; a solution outside of a cell is called hypertonic if it has a greater concentration of solutes than the cytosol inside the cell. Generalized mechanism of osmotic stress response in plants. An enzyme is a form of DNA. When a cell is in this state it is known as a turgid cell. Students can go through this article and find definitions of plant movements, types of movement in plants, seismonastic movement and much more. 3. A. Place the egg in a saturated solution (hypertonic) of sodium chloride for about 3 hours. This occurs when the cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (which has more solutes). Answer to Question #1. gamete. the remains (or an impression) of a plant or animal that existed in a past geological age and that has been excavated from the soil. PHSchool.com was retired due to Adobes decision to stop supporting Flash in 2020. This can be contrasted to the effects of a hypertonic solution, in which water molecules leave the cell, or a hypotonic solution in which water What happens to a plant cell when placed in an isotonic solution? This increases the pressure potential. lipid. A plant uses carbon dioxide, water, and sun energy to create byproducts of glucose and oxygen.
What is the tonicity of the solution compared to the cell? The Journal of Emergency Medicine is an international, peer-reviewed publication featuring original contributions of interest to both the academic and practicing emergency physician.JEM, published monthly, contains research papers and clinical studies as well as articles focusing on the training of emergency physicians and on the practice of emergency Generalized mechanism of osmotic stress response in plants. Large amounts may result in fluid overload, swelling, Conclusion. Depending on the membrane and the solute, A hypertonic solution is a solution having a higher osmotic pressure when compared to other solutions. lipid. Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. It remains turgid and can function B. Ans: When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will move outside the plant cell, i.e. When water moves into a plant cell, it swells against its rigid wall. 3. The cell wall can avoid the cell bursting. If plant cells are placed in solutions of increasing solute concentration: The sol at ion which have higher concentration is called hypertonic. When water moves into a plant cell, it swells against its rigid wall. A. In biology, the tonicity of a solution usually refers to its solute concentration relative to that of another solution on the opposite side of a cell membrane; a solution outside of a cell is called hypertonic if it has a greater concentration of solutes than the cytosol inside the cell. Osmosis affects the cells differently. uncovered a critical role for the canonical nuclear protein PARP1 in the cytosol by PARylating cyclic GMP-AMP synthase to inhibit host innate immunity, representing a beginning in the study of the function of cytosolic PARP1 in other biological processes. Weegy: An enzyme is a form of: C) protein.User: 15. However, due to the cell walls of plants, the visible effects differ. Cells use ion gradients for a number of purposes. In fact, a hypotonic solution is ideal for a plant cell. Plant roots absorb water from soil due to osmosis. Osmotic pressure is the main agent of support in many plants. The key difference between hypotonic and hypertonic is that hypotonic solution has a low solute concentration than the cell while hypertonic solution has a high solute concentration than the cell.. Osmosis is the process of moving water molecules from high water potential to low water potential through a semi-permeable membrane. Animal cells, especially nerve cells, rely on a hypertonic However, due to the cell walls of plants, the visible effects differ. Figure 35.2. 2. 2. It causes water to move into the cell and is the optimal solution for plant cells. Plasmolysis occurs due to. So, Plasmolysis in plant cells occurs due to exosmosis. Plasmolysis is the process in which cells lose water in a hypertonic solution. Fig. What is Hypertonic. Large amounts may result in fluid overload, swelling, Concentration of cell sap inside the root hair cells is higher than that of water present in the soil. What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution?
How to make a model of a Cell membrane invaginates along with the material . What is the tonicity of the solution compared to the cell? Ans: When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will move outside the plant cell, i.e. Osmotic pressure is the main agent of support in many plants. The cell expands as water comes into the cell of the plant. berkpixels/Getty Images. a.Diffusion b. Endosmosis c. Exosmosis d. Absorption 13. Photosynthetic cells can be found in chlorophyll, the green coloring on plant leaves. Photosynthetic cells can be found in chlorophyll, the The layer of the cells is thusly planned to the cell mass of the plant. When a cell is in this state it is known as a turgid cell. The osmotic entry of water raises the turgor pressure exerted against the cell wall, until it equals the osmotic pressure, creating a steady state.. An enzyme is a form of DNA. Water is lost from the cytoplasm and then from the vacuole. Thus water molecules move from inside to outside the cell. If a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the cell will shrink due to water osmotically moving out. berkpixels/Getty Images. There are three terms used to describe tonicity when comparing two solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic. Conclusion. Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. Plant cells are referred to as flaccid when in an isotonic fluid. A plant cell is placed in an aqueous solution. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. However, this semi The layer of the cells is thusly planned to the cell mass of the plant. Water always moves from a region of low to high osmolarity. When a cell is put in a hypertonic solution, water escapes the cell and flows into the surrounding solution, causing the cell to shrink and lose its turgidity. The plant cell has thick walls and requires more water. Plasma membrane c. Cell wall d. Nuclear membrane 11. Examples of osmosis in the body include the reabsorption of water by nephron tubules in the kidneys and the reabsorption of fluid at tissue capillaries. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. Animal cells, especially nerve cells, rely on a hypertonic Water floods the cell, and the cell becomes rigid with pressure. This can be contrasted to the effects of a hypertonic solution, in which water molecules leave the cell, or a hypotonic solution in which water What happens to a plant cell when placed in an isotonic solution? Plasmolysis is the shrinkage of the cytoplasm in a hypertonic medium. The effects of isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic extracellular environments on plant and animal cells is the same. This exosmosis causes shrinkage of protoplasm, i.e. 35.2 depicts the generalized mechanism of plants response under the conditions of osmotic stress. In this article, we have provided detailed information on plant movements. The direction that water moves is dependent upon the osmolarity of the solutions on either side of a semipermeable membrane.
Hypertonic-when two solution have differcut sdute concentration. This occurs when the cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (which has more solutes). This movement of ions and water is extremely important to cells. A hypertonic solution has a greater concentration of non-permeating solutes than another solution. Cells use ion gradients for a number of purposes. When a plant cell is placed in a solution that is hypertonic relative to the cytoplasm, water moves out of the cell and the cell shrinks. In fact, a hypotonic solution is ideal for a plant cell. There are three terms used to describe tonicity when comparing two solutions: hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic. Semipermeable membrane is a type of biological or synthetic, polymeric membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis.The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecules or solutes on either side, as well as the permeability of the membrane to each solute. In this condition, the cell membrane detaches from the cell wall and constricts the cytoplasm. Plasmolysis is the shrinkage of the cytoplasm in a hypertonic medium. The direction that water moves is dependent upon the osmolarity of the solutions on either side of a semipermeable membrane. How to make a model of a This exosmosis causes shrinkage of protoplasm, i.e. The outside solution has higher soluble concentration than inside the cell. When a cell is kept in a hypertonic solution, it shrinks and exosmosis occurs. Plant cells are referred to as flaccid when in an isotonic fluid. If plant cells are placed in solutions of increasing solute concentration: The key difference between hypotonic and hypertonic is that hypotonic solution has a low solute concentration than the cell while hypertonic solution has a high solute concentration than the cell.. Osmosis is the process of moving water molecules from high water potential to low water potential through a semi-permeable membrane. Examples of plant movements include roots growing downward, stomata opening and closing, petals opening, etc. Depending on the membrane and the solute, Photosynthetic cells can be found in chlorophyll, the Exocytosis: 35.2 depicts the generalized mechanism of plants response under the conditions of osmotic stress. Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. Figure 8.13 The turgor pressure within a plant cell depends on the tonicity of the solution that it is bathed in. Place the egg in a saturated solution (hypertonic) of sodium chloride for about 3 hours. When a cell is kept in a hypertonic solution, it shrinks and exosmosis occurs. A plant cell is placed in an aqueous solution. the remains (or an impression) of a plant or animal that existed in a past geological age and that has been excavated from the soil. Hypotonic-in two solation which have lawer solute con centration is called hypotonic. Cell membrane invaginates along with the material . protein. A. Isotonic B. Hypertonic C. Hypotonic. The cells will not burst when placed in a hypotonic solution. exosmosis takes place. If plant cells are placed in solutions of increasing solute concentration: This increases the pressure potential. Exocytosis: Animal cells, especially nerve cells, rely on a hypertonic Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration of electrolytes (salts in solution which in this case is represented by body fluid) to keep the body fluids from becoming too diluted or Weegy: Isotonic environment results from an equal amount of solute and solvent in and out of the cell.User: 14. Plasma membrane c. Cell wall d. Nuclear membrane 11. Home thermic-Animals who have a constant body temperature are called home thermo cot warmblooded animal. For example, plant cells use a hypertonic solution within their central vacuole to help draw water into the vacuole.This expands the chamber and allows plants to create turgor pressure in their cells. Please contact Savvas Learning Company for product support. The cells will not burst when placed in a hypotonic solution. Plant cells are referred to as flaccid when in an isotonic fluid. Hypertonic-when two solution have differcut sdute concentration. Osmosis affects the cells differently. The key difference between hypotonic and hypertonic is that hypotonic solution has a low solute concentration than the cell while hypertonic solution has a high solute concentration than the cell.. Osmosis is the process of moving water molecules from high water potential to low water potential through a semi-permeable membrane. The Journal of Emergency Medicine is an international, peer-reviewed publication featuring original contributions of interest to both the academic and practicing emergency physician.JEM, published monthly, contains research papers and clinical studies as well as articles focusing on the training of emergency physicians and on the practice of emergency Plasmolysis is when plant cells lose water after being placed in a solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than the cell does. If it is a solution it is called as pinocytosis (cell drinking) iii. Plant roots absorb water from soil due to osmosis. In this article, we have provided detailed information on plant movements. Water moving across plant cell membranes by osmosis helps to restore the plant to an erect position. whereas hypertonic causes cell growth. When water enters a plant cell by diffusion and exerts a pressure on the walls of the cell, the cell is termed as turgid. What happens in a hypertonic solution is osmosis. This process, called plasmolysis, causes plants to lose turgor pressure (Figure 8.14).
Concentration of cell sap inside the root hair cells is higher than that of water present in the soil. The cell wall can avoid the cell bursting. This process, called plasmolysis, causes plants to lose turgor pressure (Figure 8.14). Plasmolysis is the shrinkage of the cytoplasm in a hypertonic medium. Although some effects can be seen, the rigid cell wall can hide the magnitude of what is going on inside.. Osmosis and Diffusion.
The sol at ion which have higher concentration is called hypertonic. Weegy: Isotonic environment results from an equal amount of solute and solvent in and out of the cell.User: 14. Water floods the cell, and the cell becomes rigid with pressure. Hypertonic A solution of higher concentration that the solution it is being compared to.
gamete. Osmoregulation is the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids, detected by osmoreceptors, to maintain the homeostasis of the organism's water content; that is, it maintains the fluid balance and the concentration of electrolytes (salts in solution which in this case is represented by body fluid) to keep the body fluids from becoming too diluted or Examples of plant movements include roots growing downward, stomata opening and closing, petals opening, etc. Pinched off material inside the cell forms a vesicle and leaving cell membrane intact a. Water floods the cell, and the cell becomes rigid with pressure. It causes water to move into the cell and is the optimal solution for plant cells. So, Plasmolysis in plant cells occurs due to exosmosis. The cell wall is fully permeable to all molecules and supports the cell and stops it bursting when it gains water by osmosis. Water always moves from a region of low to high osmolarity. Water is lost from the cytoplasm and then from the vacuole. Examples of osmosis in the body include the reabsorption of water by nephron tubules in the kidneys and the reabsorption of fluid at tissue capillaries. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. Q.2.








