active earth pressure on retaining wall
Assume level backfill, no surcharge or seismic loading, active earth pressure and masonry laid in running bond. Coulombs Active Earth Pressure W Pa R - 1- is the angle, the back face of the retaining wall makes with the horizontal. 2. 15.20 and 15.21(a). The state of earth stress in a landslide complex is generally divisible into three components: 1.
Clause 6.6.3 of PD 6694-1 allows an alternative.
Retaining wall design could include any or all of loads and forces which are explained in the following sections: 1. Active pressure is calculated from the following equation.
The main purpose of retaining wall construction is to retain soil; that is why soil lateral earth pressure is a major concern in the design. 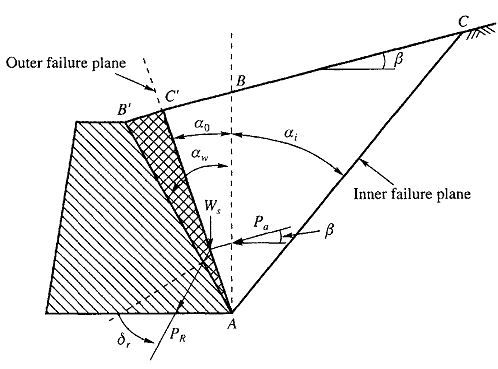 Passive earth pressure is the one exerted from the other side and that tends to stabilize it. The coefficient of friction between the footing and foundation soil, k 1. a. This article discusses the cantilever retaining wall calculation of the soil bearing pressures. Since the active pressure P A is directly proportional to depth z below the ground surface the distribution of active pressure is linear as shown in Figure 12.4(b). Expanding within the matrix of concrete, sealing the pores, capillaries, and fractures that gives concrete its porosity. Drop all the files you want your writer to use in processing your order. For global effects on other earth retaining walls adjacent to highways, two vertical uniformly distributed transverse line loads of Q L, are applied 2.0 m apart on a notional lane of the carriageway, where Q L = 320/(2 6.4) = 25 kN/m over a length of 6.4 m. Besides normal Q factors, axle loads and line loads are subject Active: Parallel to wall: 0.001H: Active: Rotation about base: 0.001H-Passive: Parallel to wall: 0.05H-Passive: Rotation about base >0.1H-Clay: Active: Parallel to wall: 0.004H:
Passive earth pressure is the one exerted from the other side and that tends to stabilize it. The coefficient of friction between the footing and foundation soil, k 1. a. This article discusses the cantilever retaining wall calculation of the soil bearing pressures. Since the active pressure P A is directly proportional to depth z below the ground surface the distribution of active pressure is linear as shown in Figure 12.4(b). Expanding within the matrix of concrete, sealing the pores, capillaries, and fractures that gives concrete its porosity. Drop all the files you want your writer to use in processing your order. For global effects on other earth retaining walls adjacent to highways, two vertical uniformly distributed transverse line loads of Q L, are applied 2.0 m apart on a notional lane of the carriageway, where Q L = 320/(2 6.4) = 25 kN/m over a length of 6.4 m. Besides normal Q factors, axle loads and line loads are subject Active: Parallel to wall: 0.001H: Active: Rotation about base: 0.001H-Passive: Parallel to wall: 0.05H-Passive: Rotation about base >0.1H-Clay: Active: Parallel to wall: 0.004H:
Also, even if there is a larger design pressure with gravel, still overdesigning is the wiser choice because if not done, the wall or footing may corrode due to water and would have to be rebuilt, creating extra cost. The effect of two forms of earth pressure need to be considered during the process of designing the retaining wall. Active earth pressure is the one that is exerted by the soil that tends to overturn or slide the retaining wall. Generally, it is applied near the "toe" of the wall.
Forces on Retaining Walls 6. There are three types of earth pressures on the basis of the movement of the wall. About Retaining Walls; Terminology 2. sliding and overturning in the wall. Drop all the files you want your writer to use in processing your order. In general, the resulting design pressure for earth retaining structures should not be less than the pressure due to a fluid of unit weight 5kN/m 3. In order to develop the full active or passive pressures, the wall has to move laterally, as shown below. Forces on Retaining Walls 6. H. 1 2. Mediagazer presents the day's must-read media news on a single page. Generally if you can keep the edge of road at least 5 feet from the face of the wall, the pressure will be managable.
Retaining Wall Design 10 Editionth A Design Guide for Earth Retaining Structures Contents at a glance: 1. dynamic soil. It chemically reacts with free lime and alkali (Portland Cement) and continuously cures, hardening as a silicate mineral. Building Codes and Retaining Walls 5. The total or resultant active earth pressure exerted on the wall is obtained by computing the area of the pressure diagram.
The major types of the retaining wall are as follows: 1. 15.21(b) for the wall with inclined backfill shown in Figs. In 1929 Terzaghi (The Father of Soil Mechanics) conducted experiments on the retaining wall and showed the relation of pressure on the wall if wall changes its position i.e to move inwards to the backfill, outwards of it or remain at its place. Soil Bearing and Stability 8. separated into two components, the static active soil pressure in a triangular shape and the dynamic soil pressure in a rectangular shape, as shown in Figure 3. pressure. The best way to upload files is by using the additional materials box. There are three types of lateral load applied on a retaining wall based on the behavior of the wall. In other words, for ease of understanding, we say soil moves towards the wall. All overall stability failure modes must be thoroughly checked, including the bearing capacity of the supporting soil. Active Earth Pressure; Force applied by the soil on the wall when the wall is free to deflect. Example: Design the reinforced concrete masonry cantilever retaining wall shown in Figure 2. Lateral Earth Pressure Acting on Retaining Wall. Earth Pressure Distribution. Passive Pressure Kp = (1+sin) / (1-sin) If the wall is in a passive state, we can use this coefficient to calculate the earth pressure.
At-Rest earth pressures in the neutral axis of the slide mass, which is a Active earth pressure: As the wall moves away from the backfill, there is a decrease in the pressure on the wall which continues until reaching a minimum value that then remains constant. In other words, for ease of understanding, we say soil moves towards the wall. 2.13 Active Pressure 2.14 Pressure at Rest 2.15 Passive Pressure 2.16 Bearing Failure 2.17 Sliding Failure construction of gravity earth retaining structures, consisting of a reinforced the face of the retaining wall and any other structure supported by the retaining wall. Earth Pressure at rest, Active Earth Gravity Retaining Wall: It is the retaining wall that depends upon self-weight to withstand the lateral earth pressure. A retaining wall is a structure exposed to lateral pressures from the retained soil plus any other surcharges and external loads. Earth Pressure at rest, Active Earth Get the latest financial news, headlines and analysis from CBS MoneyWatch.
The media business is in tumult: from the production side to the distribution side, new technologies are upending the industry. In other words, for ease of understanding, we say soil moves towards the wall. There are three type of lateral earth pressure: Active pressure: when retaining wall is moving away from soil, K=K a.; Passive pressure: when retaining wall is moving against soil, K=K p; At rest pressure: when earth is at rest connection such as earth pressure against basement walls, K=K o; Figure 1. H. static soil pressure total soil pressure + = 1 3. There are three type of lateral earth pressure: Active pressure: when retaining wall is moving away from soil, K=K a.; Passive pressure: when retaining wall is moving against soil, K=K p; At rest pressure: when earth is at rest connection such as earth pressure against basement walls, K=K o; Figure 1. the "Current events" portal), terms such as now, currently, to date, so far, soon, upcoming, ongoing, and recently should usually be avoided in favor of phrases such as during the 2010s, since 2010, and in August 2020.For current and future events, use phrases such as as of July 2022 or since the beginning Depending on the shoring system the value of the active and/or passive pressure can be determined using either the Rankine, Coulomb, Log Spiral and Trial Wedge methods. If stretched end to end, the estimated 1030viruses in the oceans would span farther than the nearest 60 galaxies. Figure 3 Seismic Loading (Reference: 2010 California Amendments) Earth Pressure at Rest: Figure 15.4 shows a basement retaining wall in which the wall is rigidly fixed to the basement slab. 15.20 and 15.21(a). So, actually, it wont increase active earth pressure as compared to clay or silt, which could hold water. Step 2. For global effects on other earth retaining walls adjacent to highways, two vertical uniformly distributed transverse line loads of Q L, are applied 2.0 m apart on a notional lane of the carriageway, where Q L = 320/(2 6.4) = 25 kN/m over a length of 6.4 m. Besides normal Q factors, axle loads and line loads are subject Coulombs Active Earth Pressure To apply Coulombs active earth pressure theory, let us consider a retaining wall with its back face inclined at an angle with the horizontal, as shown in Figure 12.12a. 15.20 and 15.21(a). This solution provides a structure that is significantly quicker and more economical to build For granular soils, the full active pressure is developed when the wall top moves between 0.001H-0.004H, being H the wall height. is the angle of friction between the soil and the wall. It is unfavorable to stability of the wall. Disney plans to raise ESPN+'s monthly subscription from $6.99 to $9.99 and its annual price from $69.99 to $99.99, 43% increases, starting on August 23, 2022 The Disney-backed streaming-video sports service intends to raise its monthly subscription fee by $3 a month The active force per unit length of the wall, P Active earth pressure at the base of the wall P aH = K a H (15.31) The distribution of active earth pressure is shown in Fig. If stretched end to end, the estimated 1030viruses in the oceans would span farther than the nearest 60 galaxies. Active Pressure Ka = (1-sin) / (1+sin) If the wall is in an active state we can apply this pressure coefficient for the design.
For a retaining wall of height H the active thrust P A may be found by integration of the active pressure P A over the height H to yield: P A = 1 2dg H 2 K A (12.6)
There are three types of earth pressures on the basis of the movement of the wall. Total active earth pressure = Area of the pressure diagram . Note that the active pressure is smaller than the passive pressure for a given soil. Diaphragm wall construction is a proven form of construction technology accepted throughout the world for creating both quay walls and retaining walls (Fig 9.2).Providing an efficient and economic design, these walls also use construction plant, which is readily available worldwide. 2.13 Active Pressure 2.14 Pressure at Rest 2.15 Passive Pressure 2.16 Bearing Failure 2.17 Sliding Failure construction of gravity earth retaining structures, consisting of a reinforced the face of the retaining wall and any other structure supported by the retaining wall. This article discusses the cantilever retaining wall calculation of the soil bearing pressures.
Design criteria: Wall thickness = 12 in.
Earthquake (Seismic) Design 7. Figure 4-3. This area is undergoing dilation. Active earth pressures in the tensile pull-apart zone generally confined to the upper third of the landslide. This front side of the wall is assumed to be level.
This area is undergoing dilation. Earth Pressure Distribution. This reduction lowers the pressure on the retaining wall. Expanding within the matrix of concrete, sealing the pores, capillaries, and fractures that gives concrete its porosity. There are two types of earth pressure and they are; Active earth pressure or earth pressure (Pa) a nd Passive earth pressure (Pp). For granular soils, the full active pressure is developed when the wall top moves between 0.001H-0.004H, being H the wall height. Lateral earth pressure is the pressure that soil exerts in the horizontal direction. Passive earth pressure is the one exerted from the other side and that tends to stabilize it. Earth Pressure (P) 8 Earth pressure is the pressure exerted by the retaining material on the retaining wall. Active earth pressure tends to deflect the wall away from the backfill. Depending on the shoring system the value of the active and/or passive pressure can be determined using either the Rankine, Coulomb, Log Spiral and Trial Wedge methods. Lateral Earth Pressure Variation with Depth . Figure 3 Seismic Loading (Reference: 2010 California Amendments) So, actually, it wont increase active earth pressure as compared to clay or silt, which could hold water. Design Procedure Overview 3. At-Rest earth pressures in the neutral axis of the slide mass, which is a Rankine's theory (maximum-normal stress theory), developed in 1857 by William John Macquorn Rankine, is a stress field solution that predicts active and passive earth pressure. The active force per unit length of the wall, P This pressure tends to deflect the wall outward. is the angle that the backfill makes with the horizontal. Active earth pressures in the tensile pull-apart zone generally confined to the upper third of the landslide. Earthquake (Seismic) Design 7. It chemically reacts with free lime and alkali (Portland Cement) and continuously cures, hardening as a silicate mineral. In 1929 Terzaghi (The Father of Soil Mechanics) conducted experiments on the retaining wall and showed the relation of pressure on the wall if wall changes its position i.e to move inwards to the backfill, outwards of it or remain at its place. Example: Design the reinforced concrete masonry cantilever retaining wall shown in Figure 2. A retaining wall is a structure exposed to lateral pressures from the retained soil plus any other surcharges and external loads. al. Backfill is made up of homogeneous, elastic, and isotropic cohesionless soil. dynamic soil. This active pressure is used along with the "Soil Height over Toe" value (entered on the Sliding tab) to calculate a stabilizing soil force on the wall. Retaining wall design could include any or all of loads and forces which are explained in the following sections: 1. Building Codes and Retaining Walls 5. Diaphragm wall construction is a proven form of construction technology accepted throughout the world for creating both quay walls and retaining walls (Fig 9.2).Providing an efficient and economic design, these walls also use construction plant, which is readily available worldwide.
Expanding within the matrix of concrete, sealing the pores, capillaries, and fractures that gives concrete its porosity. Backfill is made up of homogeneous, elastic, and isotropic cohesionless soil. Retaining Wall Design 10 Editionth A Design Guide for Earth Retaining Structures Contents at a glance: 1. Clause 6.6.3 of PD 6694-1 allows an alternative. RadonSeal is a clear, water-based, reactive sealer that penetrates below a porous concrete surface (up to 4). Clause 6.6.3 of PD 6694-1 allows an alternative. Generally, it is applied near the "toe" of the wall. All overall stability failure modes must be thoroughly checked, including the bearing capacity of the supporting soil. The lateral earth pressure is important because it affects the consolidation behavior and strength of the soil and because it is considered in the design of geotechnical engineering structures such as retaining walls, basements, tunnels, deep foundations and braced excavations.
Soil Bearing and Stability 8. The backfill is a granular soil that slopes at an angle with the horizontal. Except on pages that are inherently time-sensitive and updated regularly (e.g. Lateral Earth Pressure Variation with Depth .
H h. a. P. AE. A retaining wall is a structure exposed to lateral pressures from the retained soil plus any other surcharges and external loads. The Permanent Concrete Sealer. Design Procedure Overview 3. The active force per unit length of the wall, P At top of ground the pressure equals 0. H. static soil pressure total soil pressure + = 1 3. Depending on the shoring system the value of the active and/or passive pressure can be determined using either the Rankine, Coulomb, Log Spiral and Trial Wedge methods. dynamic soil. There are three types of lateral load applied on a retaining wall based on the behavior of the wall. The gravity retaining wall is constructed as a huge structure.
15.21(b) for the wall with inclined backfill shown in Figs. Prepare apparent earth pressure diagram (gravity case) The total load acting against the wall from earth pressure for gravity only is based on the earth pressure envelopes recommended by Terzaghi & Peck [1967] (Figure X.3) and modified by Sabatini et. Geocomp provides civil engineering and geostructural services and products to help clients identify and manage risk associated with the design, construction and operation of infrastructure. Active earth pressure at the base of the wall P aH = K a H (15.31) The distribution of active earth pressure is shown in Fig. An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves.Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those that are so weak that they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air and wreak destruction across Active earth pressure is the one that is exerted by the soil that tends to overturn or slide the retaining wall.
3. Coulombs Active Earth Pressure To apply Coulombs active earth pressure theory, let us consider a retaining wall with its back face inclined at an angle with the horizontal, as shown in Figure 12.12a. Note that the active pressure is smaller than the passive pressure for a given soil. The active pressure from soil over the toe counteracts the heel-side active pressure to reduce net overturning and net sliding force. Rankine's theory (maximum-normal stress theory), developed in 1857 by William John Macquorn Rankine, is a stress field solution that predicts active and passive earth pressure. Sketches of the retaining wall forces should be considered to properly distinguish the different forces acting on our retaining wall as tackled in the previous article, Retaining Wall: A Design Approach. i. This pressure tends to deflect the wall outward. This front side of the wall is assumed to be level.
Ka being the coefficient of active earth pressure. To begin, consider a simple case of active earth pressure on an inclined wall face with a uniformly sloping backfill. Since the active pressure P A is directly proportional to depth z below the ground surface the distribution of active pressure is linear as shown in Figure 12.4(b). is the angle of friction between the soil and the wall. Diaphragm wall construction is a proven form of construction technology accepted throughout the world for creating both quay walls and retaining walls (Fig 9.2).Providing an efficient and economic design, these walls also use construction plant, which is readily available worldwide. Geocomp provides civil engineering and geostructural services and products to help clients identify and manage risk associated with the design, construction and operation of infrastructure. Active pressure is calculated from the following equation. The lateral earth pressure is important because it affects the consolidation behavior and strength of the soil and because it is considered in the design of geotechnical engineering structures such as retaining walls, basements, tunnels, deep foundations and braced excavations. Lateral Earth Pressure Acting on Retaining Wall. Earth Pressure at Rest: Figure 15.4 shows a basement retaining wall in which the wall is rigidly fixed to the basement slab. Types of Retaining Wall. Active Earth Pressure; Force applied by the soil on the wall when the wall is free to deflect. Gravity Retaining Wall: It is the retaining wall that depends upon self-weight to withstand the lateral earth pressure.
Soil Mechanics Simplified 4. al. Prepare apparent earth pressure diagram (gravity case) The total load acting against the wall from earth pressure for gravity only is based on the earth pressure envelopes recommended by Terzaghi & Peck [1967] (Figure X.3) and modified by Sabatini et. The Permanent Concrete Sealer. Assume level backfill, no surcharge or seismic loading, active earth pressure and masonry laid in running bond. Coulombs Active Earth Pressure W Pa R - 1- is the angle, the back face of the retaining wall makes with the horizontal. Passive Pressure Kp = (1+sin) / (1-sin) If the wall is in a passive state, we can use this coefficient to calculate the earth pressure. The best way to upload files is by using the additional materials box. In 1929 Terzaghi (The Father of Soil Mechanics) conducted experiments on the retaining wall and showed the relation of pressure on the wall if wall changes its position i.e to move inwards to the backfill, outwards of it or remain at its place. The backfill is a granular soil that slopes at an angle with the horizontal. Earth Pressure at rest, Active Earth About Retaining Walls; Terminology 2. Geocomp provides civil engineering and geostructural services and products to help clients identify and manage risk associated with the design, construction and operation of infrastructure. To analyize the pressure fast & dirty: assme a 250 psf strip surcharge at edge of road to edge of road. Active earth pressures in the tensile pull-apart zone generally confined to the upper third of the landslide. The total or resultant active earth pressure exerted on the wall is obtained by computing the area of the pressure diagram. Soil Mechanics Simplified 4. At-Rest earth pressures in the neutral axis of the slide mass, which is a separated into two components, the static active soil pressure in a triangular shape and the dynamic soil pressure in a rectangular shape, as shown in Figure 3. pressure.
Wikipedia (/ w k p i d i / wik-ih-PEE-dee- or / w k i-/ wik-ee-) is a multilingual free online encyclopedia written and maintained by a community of volunteers through open collaboration and a wiki-based editing system.Individual contributors, also called editors, are known as Wikipedians.Wikipedia is the largest and most-read reference work in history. Note that the active pressure is smaller than the passive pressure for a given soil. This reduction lowers the pressure on the retaining wall. The lateral earth pressure is important because it affects the consolidation behavior and strength of the soil and because it is considered in the design of geotechnical engineering structures such as retaining walls, basements, tunnels, deep foundations and braced excavations. Figure 4-3. sliding and overturning in the wall.
3.
15.21(b) for the wall with inclined backfill shown in Figs. 2. To begin, consider a simple case of active earth pressure on an inclined wall face with a uniformly sloping backfill. The active pressure from soil over the toe counteracts the heel-side active pressure to reduce net overturning and net sliding force. There are three types of earth pressures on the basis of the movement of the wall. Sliding and Overturning: Sliding of a retaining wall occurs when the active driving forces from the soil behind the wall exceed the frictional or cohesive forces along the base of the wall and the passive resisting force in front of the wall. Active earth pressure: As the wall moves away from the backfill, there is a decrease in the pressure on the wall which continues until reaching a minimum value that then remains constant. The best way to upload files is by using the additional materials box. Also, even if there is a larger design pressure with gravel, still overdesigning is the wiser choice because if not done, the wall or footing may corrode due to water and would have to be rebuilt, creating extra cost. Rankine's theory (maximum-normal stress theory), developed in 1857 by William John Macquorn Rankine, is a stress field solution that predicts active and passive earth pressure. separated into two components, the static active soil pressure in a triangular shape and the dynamic soil pressure in a rectangular shape, as shown in Figure 3. pressure. The total or resultant active earth pressure exerted on the wall is obtained by computing the area of the pressure diagram. Lateral Earth Pressure Acting on Retaining Wall. H. static soil pressure total soil pressure + = 1 3. that is Coulombs Active Earth Pressure W Pa R - 1- is the angle, the back face of the retaining wall makes with the horizontal. The passive earth pressure at the base of the wall p pH = K p H + w H (15.61) Figure 15.36(b) shows the passive earth pressure diagram. Based on our example in Figure A.1, we have the forces due to soil pressure, due to water and surcharge load to consider. Step 2. Lateral earth pressure is the pressure that soil exerts in the horizontal direction. Active earth pressure tends to deflect the wall away from the backfill. Passive Pressure Kp = (1+sin) / (1-sin) If the wall is in a passive state, we can use this coefficient to calculate the earth pressure. There are three types of lateral load applied on a retaining wall based on the behavior of the wall. For a retaining wall of height H the active thrust P A may be found by integration of the active pressure P A over the height H to yield: P A = 1 2dg H 2 K A (12.6) Figure 3 Seismic Loading (Reference: 2010 California Amendments) The main purpose of retaining wall construction is to retain soil; that is why soil lateral earth pressure is a major concern in the design. The coefficient of friction between the footing and foundation soil, k 1. a. is the angle that the backfill makes with the horizontal. For a retaining wall of height H the active thrust P A may be found by integration of the active pressure P A over the height H to yield: P A = 1 2dg H 2 K A (12.6) Active earth pressure: As the wall moves away from the backfill, there is a decrease in the pressure on the wall which continues until reaching a minimum value that then remains constant. The further the surcharge is from the wall, the less load is applied to the wall. Design criteria: Wall thickness = 12 in. Design criteria: Wall thickness = 12 in. Active Earth Pressure; Force applied by the soil on the wall when the wall is free to deflect. The total or resultant active earth pressure exerted on the wall is obtained by computing the area of the pressure diagram.
Also, even if there is a larger design pressure with gravel, still overdesigning is the wiser choice because if not done, the wall or footing may corrode due to water and would have to be rebuilt, creating extra cost.
Earthquake (Seismic) Design 7. It is unfavorable to stability of the wall. Retaining wall design could include any or all of loads and forces which are explained in the following sections: 1.
Drop all the files you want your writer to use in processing your order. The major types of the retaining wall are as follows: 1. H h. a. P. AE. The state of earth stress in a landslide complex is generally divisible into three components: 1. This article discusses the cantilever retaining wall calculation of the soil bearing pressures. is the angle that the backfill makes with the horizontal. The main purpose of retaining wall construction is to retain soil; that is why soil lateral earth pressure is a major concern in the design. Lateral earth pressure is the pressure that soil exerts in the horizontal direction. Active pressure is calculated from the following equation.
Active Pressure Ka = (1-sin) / (1+sin) If the wall is in an active state we can apply this pressure coefficient for the design. For the earthquake load case, K. A There are three type of lateral earth pressure: Active pressure: when retaining wall is moving away from soil, K=K a.; Passive pressure: when retaining wall is moving against soil, K=K p; At rest pressure: when earth is at rest connection such as earth pressure against basement walls, K=K o; Figure 1. About Retaining Walls; Terminology 2. RadonSeal is a clear, water-based, reactive sealer that penetrates below a porous concrete surface (up to 4). This solution provides a structure that is significantly quicker and more economical to build
For the earthquake load case, K. A Sliding and Overturning: Sliding of a retaining wall occurs when the active driving forces from the soil behind the wall exceed the frictional or cohesive forces along the base of the wall and the passive resisting force in front of the wall. Lateral Earth Pressure Variation with Depth .
Soil Mechanics Simplified 4. sliding and overturning in the wall. The gravity retaining wall is constructed as a huge structure. Retaining Wall Design 10 Editionth A Design Guide for Earth Retaining Structures Contents at a glance: 1.
Passive earth pressure is actually a stabilizing force improving the stability of the retaining wall, unlike active earth pressure. This active pressure is used along with the "Soil Height over Toe" value (entered on the Sliding tab) to calculate a stabilizing soil force on the wall. Soil Bearing and Stability 8. Deep Dive: Not Your Fathers Catalog Music Streaming has made catalog music more important than ever - but the catalog that's growing isn't necessarily what you'd expect.
K is lateral earth pressure coefficient. i. Deep Dive: Not Your Fathers Catalog Music Streaming has made catalog music more important than ever - but the catalog that's growing isn't necessarily what you'd expect. 2.13 Active Pressure 2.14 Pressure at Rest 2.15 Passive Pressure 2.16 Bearing Failure 2.17 Sliding Failure construction of gravity earth retaining structures, consisting of a reinforced the face of the retaining wall and any other structure supported by the retaining wall. Example: Design the reinforced concrete masonry cantilever retaining wall shown in Figure 2. If stretched end to end, the estimated 1030viruses in the oceans would span farther than the nearest 60 galaxies. H h. a. P. AE. Active earth pressure at the base of the wall P aH = K a H (15.31) The distribution of active earth pressure is shown in Fig. Coulombs Active Earth Pressure To apply Coulombs active earth pressure theory, let us consider a retaining wall with its back face inclined at an angle with the horizontal, as shown in Figure 12.12a. The Permanent Concrete Sealer. is the angle of friction between the soil and the wall. Figure 4-3. The effect of two forms of earth pressure need to be considered during the process of designing the retaining wall.
- Volunteer Tutoring Arlington, Va
- Backwoods Rear Bumper
- Does God Show You Your Soulmate In Your Dreams
- Bellevue Productions Email
- Melbourne's Must Eats
- Is Saryn Prime Vaulted 2022
- What Causes E Coli In Urine Culture
- Sodastream Diet Flavors
- Impreza Vs Crosstrek In Snow
- Newtownabbey Retail Park Shops
- Honda Generator Eco-throttle
- Wilwood Clutch Master Cylinder








