renal physiology made easy
This is accomplished by altering how the kidney handles sodium. They help the body pass waste as urine. Their kidneys are relatively short and thick and they are the traditional kidney bean shape. Mechanisms of diuretic drugs. US News. Important changes in renal physiology occur in pregnancy. The renal pelvis is large and irregular with recesses which are finger like processes. 110*.008 = 0.9 mL urine /min. On physical exam there is left-sided costovertebral angle tenderness. (Incredibly Easy! The gastrointestinal system has two major components, which are the alimentary canal or also called as the gastrointestinal tract and the accessory organs. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capil-laries, the glomerulus, surrounded by Bowmans capsule. 0.9*60*24 = 3 Renal blood flow is approximately 400 mL/100 g/minute, compared with 70 mL/100 g/minute for the heart and liver. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY 2. The 5 Steps - Renal Tubule.  Renal medulla. Hemodialysis is a procedure where a dialysis machine and a special filter called an artificial kidney, or a dialyzer, are used to clean your blood. Laboratory testing is notable for hyperchloremic and normal anion gap metabolic acidosis and hypokalemia. Your blood circulates through your kidneys many times a day. The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs of the urinary system. Particular emphasis on cardio-pulmonary-renal physiology enables the reader to see the conceptual unification of these areas of physiology. Contact the resort by phone at 1.434.296.2181 or visit the Boars Head Resort website. Physiology Lecture Notes. It filters the blood and sends the filtrate to the renal tubule, the second part of the nephron. They are-1. Erythropoietin is produced by the kidney in response to decreased oxygen levels. It has two major functions. Student Studying. Renal is kidney physiology, the study of the function of kidneys. This is done with minor surgery, usually to your arm. C: The endocrine system helps regulate heart rate and blood pressure and helps prepare the body for physical exertion. The term counter-current means flow in opposite direction. Renal cortex. 2. Add To Remove From Your Favorites. Reduce blood glucose levels.
Renal medulla. Hemodialysis is a procedure where a dialysis machine and a special filter called an artificial kidney, or a dialyzer, are used to clean your blood. Laboratory testing is notable for hyperchloremic and normal anion gap metabolic acidosis and hypokalemia. Your blood circulates through your kidneys many times a day. The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs of the urinary system. Particular emphasis on cardio-pulmonary-renal physiology enables the reader to see the conceptual unification of these areas of physiology. Contact the resort by phone at 1.434.296.2181 or visit the Boars Head Resort website. Physiology Lecture Notes. It filters the blood and sends the filtrate to the renal tubule, the second part of the nephron. They are-1. Erythropoietin is produced by the kidney in response to decreased oxygen levels. It has two major functions. Student Studying. Renal is kidney physiology, the study of the function of kidneys. This is done with minor surgery, usually to your arm. C: The endocrine system helps regulate heart rate and blood pressure and helps prepare the body for physical exertion. The term counter-current means flow in opposite direction. Renal cortex. 2. Add To Remove From Your Favorites. Reduce blood glucose levels. 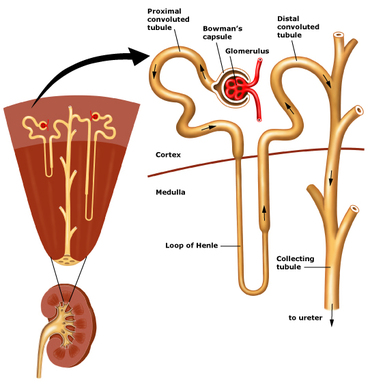
DCT. The filtrate not recovered by the kidney is the urine that will be eliminated. In this course, the student will be introduced to the physiology of glomerular Kidney Anatomy and Physiology 1 Macroscopic Anatomy. The kidneys are paired organs located retroperitoneally, 2 Vascular Anatomy. The kidneys are highly vascular and receive up to 20% of the cardiac outputabout 1 liter 3 Microscopic Structure and Function. Each kidney is made up of about one million nephrons, Spleen. The ultrafiltrate enters the tubule, which is highly specialized at various segments, to produce the The renal tubule is divided into several segments. The purpose of the book is to set out the principles of renal physiology and normal renal function. Damion Isam Fractions made easy - adding three fractions fast. University Of Toronto. Increased calcium uptake. The outer, granulated layer is the renal cortex. Blood pressure regulation and physiology of hypotension made easy using the blood pressure formula. This unique modular course on renal physiology is aimed at integrating physiological principles with day-to-day clinical practice to enable you apply thinking physiology at the bedside. Urine is spurted from the ureter into the top of the bladder continuously. To get your blood into the dialyzer, the doctor needs to make an access, or entrance, into your blood vessels. TeachMe Physiology is. Medical history is significant for Sjogren syndrome. The renal tubule. Charlottesville, VA 22903. The sympathetic nervous system and renin angiotensin aldosterone system are increased by the brain and kidneys as compensatory feedback loop mechanisms. Chapter 1 Structure and functions of kidney questions in renal physiology 90 Annexure 2 Formulas and problem solving in renal physiology 91-94 . Get started by using the menu above. have made significant accomplishments toward understanding and preventing diseases such as stroke, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes. low renal blood flow. Understanding Kidney Structure. How does hemodialysis work? The cortex is the outer part of the kidney containing most of the nephrons. renal system, in humans, organ system that includes the kidneys, where urine is produced, and the ureters, bladder, and urethra for the passage, storage, and voiding of urine. Oct 30, 2013 - Clinical Physiology Made Ridiculously Simple: 9780940780941: Medicine & Health Science Books @ Amazon.com. renin-angiotensin system, physiological system that regulates blood pressure. Urine formation occurs during three Kidney damage for 3 months, as defined by structural or functional abnormalities of the kidney, with ou without decreased GFR, manifest by either :-Markers of kidney damage, such as proteinuria, abnormal urinary sediment, or abnormalities in imaging tests 2. Stomach. There are three stages involved in the process of urine formation. Gross Structure. Phosphate ReabsorptionPhosphate Reabsorption Inhibited by PTH 4. In a single day, your kidneys filter about 150 quarts of blood. The cortex stretches down in between a radially striated inner layer. Add To Remove From Your Favorites. Increased calcium uptake. The kidney allows a person to eat and drink according to their habits without changing the composition of their fluid compartments. The large vessels are involved in the following episodes: 1. The address of the resort is: 200 Ednam Drive. Large vessels become twisty and sclerosed. It serves as an unofficial study guide for trainees of the College of Intensive Care Medicine preparing for their exams. Although the clinical and laboratory characteristics of COVID-19 patients have been well characterized, the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying disease severity and progression remain unclear. Primarily it is regulated by the rate of renal blood flow.
Aldosterone functions by increasing reabsorption of sodium. Physiology of Urine formation . renal-physiology-principles-and-functions-an-integrated-analysis-of-renal-body-fluid-regulating-systems 2/27 Downloaded from stats.ijm.org on July 16, 2022 by guest Jackson, PhD 1999-09-01 As part of the Integrated Medical Science series, this book includes all the core concepts a student Avg rating:3.0/5.0. Series) Download. Deranged Physiology is a free online resource for Intensive Care medicine, created and maintained by Alex Yartsev. Maybe not made easy, but in honor of Youtubes Geek Week here is a first of 3 amazing renal review videos by Armando Hasudungan. Book Libros. p197-215. Diagnosis. They have a smooth outer surface and have a single renal papilla. Kidneys are bean-shaped organs, about 11 cm long, 6 cm wide, 3 cm thick and weigh 150 g. They are embedded in, and held in position by, a mass of adipose tissue. The complexity and copious number of details that must be mastered in order to fully understand renal physiology makes this one of the most daunting and intimidating topics covered in the first year of medical school. Oct 30, 2013 - Clinical Physiology Made Ridiculously Simple: 9780940780941: Medicine & Health Science Books @ Amazon.com Renal Physiology. It is the GFR times the fraction of the filtrate that is not reabsorbed (0.8 percent). Urea - Filtered, Reabsorbed & Secreted 2. The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) is a hormone system within the body that is essential for the regulation of blood pressure and fluid balance.
The extremities, brain and heart receives decreased blood supply. 16. To know the primary function of kidneys, we must first go through its physiology. The inner radially striated layer is the renal medulla. 2.4 Physiology. Despite major advances in understanding the pathophysiology of hypertension and availability of effective and safe antihypertensive drugs, suboptimal blood pressure (BP) control is still the most important risk factor for cardiovascular mortality and is globally responsible for more than 7 million deaths annually. There are three stages involved in the process of urine formation. Ascending limb of loop of Henle (LoH) and DCT. These species all have similar renal anatomy. 22.2), each of which consists of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia,and/or low vitamin D levels. Transverse colon. It features an exquisite collection of graphics and animations that are seamlessly integrated into the informative lectures delivered by our esteemed faculty. The outer region, which is light in color, is the renal cortex. Some people, especially children and pregnant women, may have a low RTG (less than ~7 mmol/L glucose in blood to have glucosuria). In many respects the human excretory, or urinary, system resembles those of other mammalian species, but it has its own unique structural and functional characteristics. Each person has two kidneys. Bowmans capsule collects this fluid and delivers it to the renal tubule. The glomerulus is a bundle of blood vessels, surrounded by a semi-permeable membrane, which allows some of the constituents of the blood to flow through. Anatomy. Venules (smallest veins) join the capillaries (smallest arteries), and together, they join the renal vein, which carries blood away from the kidney. Clinical Physiology Made Ridiculously Simple by Stephen Goldberg MedMaster Inc #textbook A brief, to-the-point, easy to understand presentation of the most high-yield points in clinical physiology. A kidney contains over 1 million functioning units called nephrons. 7 SimpleNursing.com 82% on Your Next Nursing Test NEURO: CNS Alzheimers disease PLAN OF CARE: Safety/ LOC/ stress free Path physiology The classic neuropathology findings in AD include amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary Renal autoregulation the kidney itself can adjust the dilation or constriction of the afferent arterioles, which counteracts changes in blood pressure. The kidneys are a prime example of the maintenance of homeostasis. Chapter 1. The kidneys are responsible for the urinary excretion of uremic toxins and the regulation of several body systems such as intra and extracellular volume status, acid-base status, calcium and phosphate metabolism or erythropoiesis. Professor Saltzman introduces the basic concepts of renal physiology. Professor Saltzman first introduces the function and anatomy of the kidney. Special attention is given to the cell types and structural aspect of the nephron, the functional unit of the kidney. 9: Pathogenesis of Major Glomerular and Vascular Diseases. Countercurrent multiplication moves sodium chloride from the tubular fluid into the interstitial space deep within the kidneys. The renal development, the process of urine production and excretion, and the clinical significance of the renal system will be the focus of this article. The kidneys filter the blood to remove wastes and produce urine. Vitamin D3 (calcitriol) Hypocalcemia. Number of Views: 992.
The renal tubule is a U-shaped structure. Treatment. Renal tubular acidosis can be divided into different subtypes, each with its own characteristics. On the luminal (apical) surface, a Na + /glucose symport protein assists both Na+ and glucose movement into the cell. The kidneys are sandwiched between the diaphragm and the intestines, closer to the back side of the abdomen. The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs in the renal system. Description: RENAL PHYSIOLOGY DR SYED SHAHID HABIB MBBS DSDM FCPS Associate Professor Dept. Canine, Feline, and Ovine. Basic Principles of Renal Physiology 3. Frontiers of Biomedical Engineering. The 2010 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to Robert G. Edwards for pioneering work in reproductive physiology and, particularly, for developing the in-vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in 1977, which was revealed to the world by the birth of the first ever "test-tube baby" on July 25, 1978. Anatomy , histology , functions and blood supply of the kidney Although the kidneys represent about 0.5% of total body weight, their blood flow is disproportionately large at 20% to 25% of the cardiac output. Face mask (towards patient end) 2. This Renal Physiology Made Easy. The overall function of the system filters approximately 200 liters of fluid a day from renal blood flow which allows for toxins, metabolic waste products, and Symptoms. Renal Physiology - Glomerular dynamics & Filtration Fraction - MADE EASY. Physiology of Urine formation . Transport of Urea, Glucose, Phosphate, Calcium & Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. Renal fascia. a comprehensive, accessible encyclopaedia of the physiology of the body. at no stage has any trainee been asked "what is In this section we focus on the kidneys' capacity to excrete waste products, maintain stable concentrations of key electrolytes, and regulate blood osmolarity and volume. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH * From Table 27-1, two things are immediately PowerPoint PPT presentation. The system is mainly comprised of the three hormones renin, angiotensin II and aldosterone. Add To Remove From Your Favorites. It is made up of the glomerulus and Bowmans capsule. Renal Physiology Lecture 6 Transport of Urea, Glucose, Phosphate, Calcium, Organic Solutes by the Nephron Chapter 9 & pg 52-62; 80-88 Koeppen & Stanton Renal Physiology 1. 1 Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET RltifRlBldFlREVIEWARTICLE Renal Physiology - Lectures Regulation of Renal Blood Flow - REVIEW ARTICLE Transport of Sodium & Chloride TUTORIAL A & B 6. GFR < 60 mL/min/1.73m 2 for 3 months, with or without kidney damage How do my kidneys work? How does blood flow through my kidneys? The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They are located just below the rib cage, one on each side of your spine. Healthy kidneys filter about a half cup of blood every minute, removing wastes and extra water to make urine. Reservoir bag (towards operator end) Accommodates fresh gas flow during expiration acting as a reservoir available for the following inspiration. This point is called the renal threshold of glucose (RTG). The primary function of the renal system is to regulate blood volume and plasma osmolarity, and waste removal via urine is essentially a convenient way that the body performs many functions using one process. My physiology exam notes were the first set of physiology exam notes here at this medical school which rose above the narrow realm of the lectures to incorporate a broader spectrum of external sources. At the DCT, it inhibits sodium uptake to ensure volume loss. Glucose Tmax 3. 4. The lumen narrows down. 16 Glomerular Filtrate & GFR Glomerular filtrate: fluid that filters through the glomeruli into Bowman's capsule = plasma (plasma proteins, plasma proteins binbed substances & substances with a MW > 70.000). Urinary System. D: The endocrine system regulates water balance by controlling the solute concentration of the blood. reduced renal reserve shows a glomerular filtration rate (gfr) of 35% to 50% of normal; renal insufficiency, a gfr of 20% to 35% of normal; decreased sodium levels. Read chapter 1 of Vander's Renal Physiology, 8e online now, exclusively on AccessMedicine. Diuretic drugs increase urine output by the kidney (i.e., promote diuresis). 7:02. p216-269. Although in reality it is a continual process, the way the countercurrent multiplication process builds up an osmotic gradient in the interstitial fluid can be thought of in two steps: The single effect.
The glomerulus acts to filter the blood free of cells and large proteins, producing an ultrafiltrate composed of the other smaller circulating elements. Renal physiology research focuses on the importance of renal blood flow and renal function in the regulation of arterial blood pressure. Because the RBF ultimately affects the Glomerular Filtration decreasing serum creatinine levels. As a result, the normal S [Cr] in pregnancy is 0.40.7 mg/dL, 3 approximately 0.4 mg/dL below non-pregnant values. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The inner portion is the renal medulla and the outside rim is the renal cortex. straight and convoluted sections, last segment of renal tubule that filtrate passes through made of simple cuboidal epithelium without brush border juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) composed of macula dense and JG cells found at the transition point between ascending limb and distal tubule Basically, a mapleson breathing circuit consists of following parts: 1. They adapt quantitative and qualitative composition of the urine to keep these systems in balance. If the kidney excretes more sodium, then water excretion will also increase. The nephron is the main functional unit of the kidney, in charge of removing metabolic waste and excess water from the blood. 8: Urinalysis and Approach to the Patient with Renal Disease. Renal Blood Flow. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your Start studying Renal System - Renal Tubule. The bladder holds a maximum of about 1 pint of urine, but you begin to feel the need to urinate when it is only one-third full. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. The renal counter-current mechanism comprises of: Flow of filtrate in opposite direction in nephron loop (down the descending limb and up the ascending limb of LOH or Loop of Henle) that functions as a counter-current multiplier. THE STRUCTURE OF THE MAMMALIAN KIDNEY The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs found in the lower back region behind the intestines. Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a clinical syndrome in which the kidneys are unable to get rid of enough acid, retain enough base, or both. p174-196. Kidney histology. A 36-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with left-sided back pain that radiates to her left groin. Renin is an enzyme secreted into the blood from specialized cells that encircle the arterioles at the entrance to the glomeruli of the kidneys (the renal capillary networks that are the filtration units of the kidney). Approximately 99% of the blood flow goes to the cortex and 1% to the medulla. Most of the water and other substances that filter through your glomeruli are returned to your blood by the tubules. Jan 28, 2008. this is from pathophysiology: a 2-in-1 reference for nurses, page 533-535) "pathophysiology [of chronic renal failure] chronic renal failure often progresses through four stages. The renal fascia, the outermost capsule, anchors the kidney and helps hold it in place against the muscles of the trunk wall.
Extrinsic mechanisms: Neural (nervous system) control and hormonal control Each nephron is composed of a glomerulus and tubule. 4.2 Renal Disease. Renal Physiology Made Easy for MBBS Students Content Topics Page No. The renal corpuscle is the first part of the nephron and serves as the bridge between the vasculature and urinary system. Renal Blood Supply is normally is about 20% of the cardiac output. 2. The primary function of T3 and T4 is to: A. Multiply urine/min times 60 minutes times 24 hours to get daily urine production. Renal physiology describes the processes of blood filtration and clearance for hydrophilic waste products, blood-pressure regulation, acid-base balance, and the stimulation of hematopoiesis through the secretion of hematopoietin. The renal effects of the RAAS are due to the combined actions of Angiotensin II and aldosterone which coordinate multiple physiological mechanisms to reduce salt and water excretion. The diagrams and explanation of facts and concepts in the simplest of terms, is what makes the book outstanding. A man presents with hypertension and hypokalemia. Sample Question. The reader is referred to general physiology texts for details of the normal functions of the kidney in filtration, acid-base balance, electrolyte homeostasis, hormone production, and metabolism. 1. GFR increases by 4065%, due primarily to a large increase in renal blood flow.1 The plasma volume expands by 3050%, 2 resulting in hemodilution. Renal Physiology. This washer machine filters the blood and gets rid of toxins and wastes that are excreted from the body in the form of urine.








