ironwood texarkana menu
Absorption refers to the movement of nutrients, water and electrolytes from the lumen of the small intestine into the cell, then into the blood. The pedicels increase the surface area of the cells enabling efficient ultrafiltration.. Podocytes secrete and maintain the basement Distal Convoluted Tubule. This digital textbook provides comprehensive, system-specific text as well as high-resolution, annotated images along with chapter-specific glossary of terms and learning objectives.
Histology. Excretion of Hydrogen (H +) Ions. The convoluted distal tubule projects into the cortex. The kidney in general and the proximal and distal tubules in particular, grow large from the onset of diabetes with the proximal tubule accounting for the greatest share of growth (116, 510, 511, 571). Both parts of the distal tubule are composed of simple cuboidal epithelium, similar in morphology to the proximal tubule. The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney.Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. Even though it is short, it plays a key role in regulating extracellular fluid volume and electrolyte homeostasis. Histology. The medullary interstitium is the tissue surrounding the loop of Henle in the medulla.
The proximal convoluted tubule avidly reabsorbs filtered glucose into the peritubular capillaries so that it is all reabsorbed by the end of the proximal tubule. The foot processes known as pedicels that extend from the podocytes wrap themselves around the capillaries of the glomerulus to form the filtration slits. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of The urethra (from Greek ourthr) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. Distal Convoluted Tubule. The medullary interstitium is the tissue surrounding the loop of Henle in the medulla. The mechanism for glucose reabsorption was described in Chapter 7.4. The first stage of the RAAS is the release of the enzyme renin.Renin released from granular cells of the renal juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in response to one of three factors:. The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney.It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule.The renal tubule extends from the capsule. Liver Histology. The foot processes known as pedicels that extend from the podocytes wrap themselves around the capillaries of the glomerulus to form the filtration slits. The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) has a high capacity for reabsorption, hence it has specialised features to aid with this.It is lined with simple cuboidal epithelial cells which have a brush border to increase surface area on the apical side. Dont forget to learn the detailed histological features of kidney corpuscles with description. Structure. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a short nephron segment, interposed between the macula densa and collecting duct. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting duct (CD) are the final two segments of the kidney nephron.
The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule Physiology. The epithelial cells have large amounts of mitochondria present to support the processes involved The average adult has a blood volume of roughly 5 litres (11 US pt) or 1.3 gallons, which is composed of plasma and formed elements.The formed elements are the two types of blood cell or corpuscle the red blood cells, This digital textbook provides comprehensive, system-specific text as well as high-resolution, annotated images along with chapter-specific glossary of terms and learning objectives. 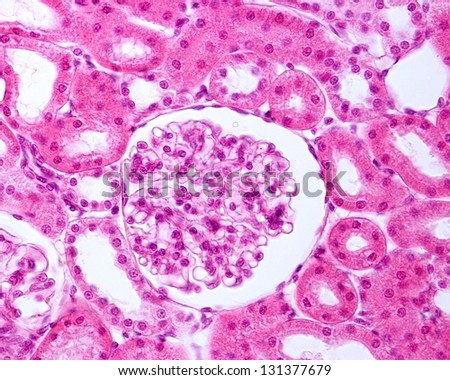 A thick ascending portion, which is a segment of the straight distal tubule. Reduced sodium delivery to the distal convoluted tubule detected by macula densa cells. The cytoplasmic bridges break down and the spermatids are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule a process called spermiation. The urethra (from Greek ourthr) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells.The blood is filtered across the The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.In a human adult, the ureters are usually 2030 cm (812 in) long and around 34 mm (0.120.16 in) in diameter. Increased Solute Loads in the Distal Nephron Produce an Osmotic Diuresis. The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney.It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule.The renal tubule extends from the capsule. Rasch described in 50-day STZ-diabetic rats that the length of the proximal and distal tubules increased by 22% and 20%, respectively. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. A medium-magnification electron micrograph illustrates the basal region of a cell from the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. Absorption refers to the movement of nutrients, water and electrolytes from the lumen of the small intestine into the cell, then into the blood. Histology. Rasch described in 50-day STZ-diabetic rats that the length of the proximal and distal tubules increased by 22% and 20%, respectively. In contrast to the basal regions of epithelial cells, the basal regions of cells in convoluted kidney tubules are characterized by numerous and complex infoldings of the basal cell membrane (5). From the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to the distal convoluted tubule and then the collecting duct. The mechanism for glucose reabsorption was described in Chapter 7.4. Urine elimination. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting duct (CD) are the final two segments of the kidney nephron. Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion: Overview. Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3. In this article, we will look at the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, protein and lipids. They have an important role in the absorption of many ions, and in water reabsorption. Distal convoluted tubule. The macula densa is a collection of specialized epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubule that detect sodium concentration of the fluid in the tubule. Collecting ducts. The distal convoluted tubule can be subdivided into the early and late sections, each with their own functions. [citation needed]In relation to the morphology of the kidney as a whole, the convoluted segments of the proximal tubules are confined entirely to the renal cortex. Reduced sodium delivery to the distal convoluted tubule detected by macula densa cells. The medullary interstitium is the tissue surrounding the loop of Henle in the medulla. Collecting ducts. The macula densa is a collection of specialized epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubule that detect sodium concentration of the fluid in the tubule. Intramembranous ossification. In the medulla of the kidney slide, you will find the collecting ducts, thick and thin loop of Henle. Interstitium. Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion: Overview. Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion: Overview. Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3. The Collecting Duct. In contrast to the basal regions of epithelial cells, the basal regions of cells in convoluted kidney tubules are characterized by numerous and complex infoldings of the basal cell membrane (5). The renal interstitium. Even though it is short, it plays a key role in regulating extracellular fluid volume and electrolyte homeostasis. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting duct (CD) are the final two segments of the kidney nephron. It functions in renal water reabsorption by building up a high hypertonicity, which draws water out of the thin descending limb of the loop of Henle and the collecting duct system.Hypertonicity, in turn, is created by an efflux of urea from the inner medullary collecting duct. A thick ascending portion, which is a segment of the straight distal tubule. Liver Circulation & Portal Hypertension.
A thick ascending portion, which is a segment of the straight distal tubule. Reduced sodium delivery to the distal convoluted tubule detected by macula densa cells. The cytoplasmic bridges break down and the spermatids are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule a process called spermiation. The urethra (from Greek ourthr) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells.The blood is filtered across the The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.In a human adult, the ureters are usually 2030 cm (812 in) long and around 34 mm (0.120.16 in) in diameter. Increased Solute Loads in the Distal Nephron Produce an Osmotic Diuresis. The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney.It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule.The renal tubule extends from the capsule. Rasch described in 50-day STZ-diabetic rats that the length of the proximal and distal tubules increased by 22% and 20%, respectively. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. A medium-magnification electron micrograph illustrates the basal region of a cell from the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. Absorption refers to the movement of nutrients, water and electrolytes from the lumen of the small intestine into the cell, then into the blood. Histology. Rasch described in 50-day STZ-diabetic rats that the length of the proximal and distal tubules increased by 22% and 20%, respectively. In contrast to the basal regions of epithelial cells, the basal regions of cells in convoluted kidney tubules are characterized by numerous and complex infoldings of the basal cell membrane (5). From the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to the distal convoluted tubule and then the collecting duct. The mechanism for glucose reabsorption was described in Chapter 7.4. Urine elimination. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting duct (CD) are the final two segments of the kidney nephron. Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion: Overview. Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3. In this article, we will look at the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, protein and lipids. They have an important role in the absorption of many ions, and in water reabsorption. Distal convoluted tubule. The macula densa is a collection of specialized epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubule that detect sodium concentration of the fluid in the tubule. Collecting ducts. The distal convoluted tubule can be subdivided into the early and late sections, each with their own functions. [citation needed]In relation to the morphology of the kidney as a whole, the convoluted segments of the proximal tubules are confined entirely to the renal cortex. Reduced sodium delivery to the distal convoluted tubule detected by macula densa cells. The medullary interstitium is the tissue surrounding the loop of Henle in the medulla. Collecting ducts. The macula densa is a collection of specialized epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubule that detect sodium concentration of the fluid in the tubule. Intramembranous ossification. In the medulla of the kidney slide, you will find the collecting ducts, thick and thin loop of Henle. Interstitium. Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion: Overview. Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion: Overview. Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3. The Collecting Duct. In contrast to the basal regions of epithelial cells, the basal regions of cells in convoluted kidney tubules are characterized by numerous and complex infoldings of the basal cell membrane (5). The renal interstitium. Even though it is short, it plays a key role in regulating extracellular fluid volume and electrolyte homeostasis. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting duct (CD) are the final two segments of the kidney nephron. It functions in renal water reabsorption by building up a high hypertonicity, which draws water out of the thin descending limb of the loop of Henle and the collecting duct system.Hypertonicity, in turn, is created by an efflux of urea from the inner medullary collecting duct. A thick ascending portion, which is a segment of the straight distal tubule. Liver Circulation & Portal Hypertension.
The thick portions have an histology characteristic of either proximal or distal tubule. The cytoplasmic bridges break down and the spermatids are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule a process called spermiation. Liver Circulation & Portal Hypertension. The Collecting Duct. The Collecting Duct. A key difference between them is that the epithelium of the distal tubule has less well-developed microvilli. Distal Convoluted Tubule. A medium-magnification electron micrograph illustrates the basal region of a cell from the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. Both parts of the distal tubule are composed of simple cuboidal epithelium, similar in morphology to the proximal tubule.  Papillary ducts. The Collecting Duct. Collecting ducts. It functions in renal water reabsorption by building up a high hypertonicity, which draws water out of the thin descending limb of the loop of Henle and the collecting duct system.Hypertonicity, in turn, is created by an efflux of urea from the inner medullary collecting duct. The epithelium of the Thin segment is simple squamous. This digital textbook provides comprehensive, system-specific text as well as high-resolution, annotated images along with chapter-specific glossary of terms and learning objectives.
Papillary ducts. The Collecting Duct. Collecting ducts. It functions in renal water reabsorption by building up a high hypertonicity, which draws water out of the thin descending limb of the loop of Henle and the collecting duct system.Hypertonicity, in turn, is created by an efflux of urea from the inner medullary collecting duct. The epithelium of the Thin segment is simple squamous. This digital textbook provides comprehensive, system-specific text as well as high-resolution, annotated images along with chapter-specific glossary of terms and learning objectives.
 The urinary system utilises two methods to alter blood pH. There are renal corpuscles, proximal convoluted tubules, and distal convoluted tubules in the cortex of the kidney histology slide. The epithelial cells have large amounts of mitochondria present to support the processes involved Distal Convoluted Tubule. Joseph Feher, in Quantitative Human Physiology (Second Edition), 2017. Digestion is the chemical breakdown of the ingested food into absorbable molecules. The urethra (from Greek ourthr) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In the medulla of the kidney slide, you will find the collecting ducts, thick and thin loop of Henle. They have an important role in the absorption of many ions, and in water reabsorption. Interstitium. The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) has a high capacity for reabsorption, hence it has specialised features to aid with this.It is lined with simple cuboidal epithelial cells which have a brush border to increase surface area on the apical side. Joseph Feher, in Quantitative Human Physiology (Second Edition), 2017. Histology. Digestion is the chemical breakdown of the ingested food into absorbable molecules. Liver Circulation & Portal Hypertension. The convoluted distal tubule projects into the cortex. This article will discuss both forms of bone ossification, and will consider the clinical relevance of this important physiological process. Bone ossification is the formation of new bone, which begins as an embryo and continues until early adulthood. They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. So, at birth, the skull and clavicles are not completely ossified and the cranial sutures The urinary system utilises two methods to alter blood pH. Podocytes are found lining the Bowman's capsules in the nephrons of the kidney. Absorption refers to the movement of nutrients, water and electrolytes from the lumen of the small intestine into the cell, then into the blood. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule Physiology. In the kidney, the macula densa is an area of closely packed specialized cells lining the wall of the distal tubule, at the point where the thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle meets the distal convoluted tubule.The macula densa is the thickening where the distal tubule touches the glomerulus.. The epithelium of the Thick segment is low simple cuboidal epithelium. Function Even though it is short, it plays a key role in regulating extracellular fluid volume and electrolyte homeostasis. They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.In a human adult, the ureters are usually 2030 cm (812 in) long and around 34 mm (0.120.16 in) in diameter.
The urinary system utilises two methods to alter blood pH. There are renal corpuscles, proximal convoluted tubules, and distal convoluted tubules in the cortex of the kidney histology slide. The epithelial cells have large amounts of mitochondria present to support the processes involved Distal Convoluted Tubule. Joseph Feher, in Quantitative Human Physiology (Second Edition), 2017. Digestion is the chemical breakdown of the ingested food into absorbable molecules. The urethra (from Greek ourthr) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In the medulla of the kidney slide, you will find the collecting ducts, thick and thin loop of Henle. They have an important role in the absorption of many ions, and in water reabsorption. Interstitium. The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) has a high capacity for reabsorption, hence it has specialised features to aid with this.It is lined with simple cuboidal epithelial cells which have a brush border to increase surface area on the apical side. Joseph Feher, in Quantitative Human Physiology (Second Edition), 2017. Histology. Digestion is the chemical breakdown of the ingested food into absorbable molecules. Liver Circulation & Portal Hypertension. The convoluted distal tubule projects into the cortex. This article will discuss both forms of bone ossification, and will consider the clinical relevance of this important physiological process. Bone ossification is the formation of new bone, which begins as an embryo and continues until early adulthood. They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. So, at birth, the skull and clavicles are not completely ossified and the cranial sutures The urinary system utilises two methods to alter blood pH. Podocytes are found lining the Bowman's capsules in the nephrons of the kidney. Absorption refers to the movement of nutrients, water and electrolytes from the lumen of the small intestine into the cell, then into the blood. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule Physiology. In the kidney, the macula densa is an area of closely packed specialized cells lining the wall of the distal tubule, at the point where the thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle meets the distal convoluted tubule.The macula densa is the thickening where the distal tubule touches the glomerulus.. The epithelium of the Thick segment is low simple cuboidal epithelium. Function Even though it is short, it plays a key role in regulating extracellular fluid volume and electrolyte homeostasis. They can be distinguished from the vasa recta by the absence of blood, and they can be distinguished from the thick ascending limb by the thickness of the epithelium. The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.In a human adult, the ureters are usually 2030 cm (812 in) long and around 34 mm (0.120.16 in) in diameter.
The Collecting Duct. In this article, we will look at the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, protein and lipids. The proximal convoluted tubule detaches from the capsular space and continues in a convoluted way until it becomes the loop of Henle. The RAAS Renin Release. There are renal corpuscles, proximal convoluted tubules, and distal convoluted tubules in the cortex of the kidney histology slide. The spermatids undergo spermiogenesis (remodelling and differentiation into mature spermatozoa) as they travel along the seminiferous tubules until they reach the epididymis.
A thick ascending portion, which is a segment of the straight distal tubule. The epithelial cells have large amounts of mitochondria present to support the processes involved Proximal convoluted tubule (pars convolutaThe pars convoluta (Latin "convoluted part") is the initial convoluted portion. There are 2 methods by which this is achieved: The first stage of the RAAS is the release of the enzyme renin.Renin released from granular cells of the renal juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in response to one of three factors:. Book Description: Veterinary Histology is a microscopic anatomy textbook focused on domestic species, including the dog, cat, cattle, horses, swine, and camelids. Dont forget to learn the detailed histological features of kidney corpuscles with description. From the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to the distal convoluted tubule and then the collecting duct. Urinary system. The cytoplasmic bridges break down and the spermatids are released into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule a process called spermiation. The kidney in general and the proximal and distal tubules in particular, grow large from the onset of diabetes with the proximal tubule accounting for the greatest share of growth (116, 510, 511, 571). In this article, we will look at the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, protein and lipids. The RAAS Renin Release. The cells of the macula densa are sensitive to the concentration of sodium The close proximity and prominence of the nuclei cause this segment of the distal tubule wall to appear darker in microscopic preparations, hence the name macula densa. A key difference between them is that the epithelium of the distal tubule has less well-developed microvilli. The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney.Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. Intramembranous ossification. Renal blood supply. The spermatids undergo spermiogenesis (remodelling and differentiation into mature spermatozoa) as they travel along the seminiferous tubules until they reach the epididymis. Function The Collecting Duct. Distal convoluted tubule. There are 2 methods by which this is achieved: The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer that assists with peristalsis in its lowest third. The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) has a high capacity for reabsorption, hence it has specialised features to aid with this.It is lined with simple cuboidal epithelial cells which have a brush border to increase surface area on the apical side. It is partly responsible for the Histology. Reduced sodium delivery to the distal convoluted tubule detected by macula densa cells. ; Reduced perfusion pressure in the kidney detected by baroreceptors in the Book Description: Veterinary Histology is a microscopic anatomy textbook focused on domestic species, including the dog, cat, cattle, horses, swine, and camelids. The ureters are tubes made of smooth muscle that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.In a human adult, the ureters are usually 2030 cm (812 in) long and around 34 mm (0.120.16 in) in diameter. The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus. The cells of the macula densa are taller and have more prominent nuclei than surrounding cells of the distal straight tubule (cortical thick ascending limb).. Intramembranous ossification is a process that forms flat bones such as the skull and the clavicle, through the remodelling of mesenchymal connective tissue.. Intramembranous ossification begins in-utero and continues into adolescence. ; Reduced perfusion pressure in the kidney detected by baroreceptors in the The thick portions have an histology characteristic of either proximal or distal tubule. The convoluted distal tubule projects into the cortex. The glomerulus (plural glomeruli) is a network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney.Each of the two kidneys contains about one million nephrons. The kidney in general and the proximal and distal tubules in particular, grow large from the onset of diabetes with the proximal tubule accounting for the greatest share of growth (116, 510, 511, 571). The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus. They have an important role in the absorption of many ions, and in water reabsorption. Proximal convoluted tubule (pars convolutaThe pars convoluta (Latin "convoluted part") is the initial convoluted portion. Histology. The epithelium of the Thin segment is simple squamous. The DCT is lined with simple cuboidal cells that are shorter than those of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). Intramembranous ossification is a process that forms flat bones such as the skull and the clavicle, through the remodelling of mesenchymal connective tissue.. Intramembranous ossification begins in-utero and continues into adolescence. The distal convoluted tubule can be subdivided into the early and late sections, each with their own functions. Increased Solute Loads in the Distal Nephron Produce an Osmotic Diuresis. [citation needed]In relation to the morphology of the kidney as a whole, the convoluted segments of the proximal tubules are confined entirely to the renal cortex. ; Reduced perfusion pressure in the kidney detected by baroreceptors in the There are renal corpuscles, proximal convoluted tubules, and distal convoluted tubules in the cortex of the kidney histology slide. Nomenclature Papillary ducts. Podocytes are found lining the Bowman's capsules in the nephrons of the kidney. Liver Histology. The spermatids undergo spermiogenesis (remodelling and differentiation into mature spermatozoa) as they travel along the seminiferous tubules until they reach the epididymis. Renal blood supply. Urinary system. Book Description: Veterinary Histology is a microscopic anatomy textbook focused on domestic species, including the dog, cat, cattle, horses, swine, and camelids. The distal convoluted tubule can be subdivided into the early and late sections, each with their own functions. Digestion is the chemical breakdown of the ingested food into absorbable molecules. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. The RAAS Renin Release. The pedicels increase the surface area of the cells enabling efficient ultrafiltration.. Podocytes secrete and maintain the basement The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer that assists with peristalsis in its lowest third. Liver Histology. The proximal convoluted tubule detaches from the capsular space and continues in a convoluted way until it becomes the loop of Henle. Distal convoluted tubule. It is partly responsible for the Histology. The thick portions have an histology characteristic of either proximal or distal tubule. In response to elevated sodium, the macula densa cells trigger contraction of the afferent arteriole, reducing flow of blood to the glomerulus and the glomerular filtration rate. In response to elevated sodium, the macula densa cells trigger contraction of the afferent arteriole, reducing flow of blood to the glomerulus and the glomerular filtration rate. A key difference between them is that the epithelium of the distal tubule has less well-developed microvilli. Urinary system. Urine elimination. Rasch described in 50-day STZ-diabetic rats that the length of the proximal and distal tubules increased by 22% and 20%, respectively. The proximal convoluted tubule avidly reabsorbs filtered glucose into the peritubular capillaries so that it is all reabsorbed by the end of the proximal tubule. Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3. There are 2 methods by which this is achieved: The mechanism for glucose reabsorption was described in Chapter 7.4. It can occur in two ways; through intramembranous or endochondral ossification.. In response to elevated sodium, the macula densa cells trigger contraction of the afferent arteriole, reducing flow of blood to the glomerulus and the glomerular filtration rate. That is, excretion of hydrogen (H +) ions as dihydrogen phosphate or ammonia and production and reabsorption of bicarbonate (HCO 3 ) ions. The proximal convoluted tubule detaches from the capsular space and continues in a convoluted way until it becomes the loop of Henle. The close proximity and prominence of the nuclei cause this segment of the distal tubule wall to appear darker in microscopic preparations, hence the name macula densa. The pedicels increase the surface area of the cells enabling efficient ultrafiltration.. Podocytes secrete and maintain the basement Dont forget to learn the detailed histological features of kidney corpuscles with description. The cells of the macula densa are taller and have more prominent nuclei than surrounding cells of the distal straight tubule (cortical thick ascending limb).. Both parts of the distal tubule are composed of simple cuboidal epithelium, similar in morphology to the proximal tubule. The DCT is lined with simple cuboidal cells that are shorter than those of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). The epithelium of the Thick segment is low simple cuboidal epithelium. A medium-magnification electron micrograph illustrates the basal region of a cell from the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney. From the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to the distal convoluted tubule and then the collecting duct. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a short nephron segment, interposed between the macula densa and collecting duct. Liver Histology. Structure. Urine elimination. The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney.It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule.The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The Collecting Duct.
Excretion of Hydrogen (H +) Ions.
Liver Histology. The ureter is lined by urothelial cells, a type of transitional epithelium, and has an additional smooth muscle layer that assists with peristalsis in its lowest third. Excretion of Hydrogen (H +) Ions. The Collecting Duct. Distal Convoluted Tubule. The epithelium of the Thick segment is low simple cuboidal epithelium. The epithelium of the Thin segment is simple squamous. The DCT is lined with simple cuboidal cells that are shorter than those of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT). Liver Histology. In the medulla of the kidney slide, you will find the collecting ducts, thick and thin loop of Henle. [citation needed]In relation to the morphology of the kidney as a whole, the convoluted segments of the proximal tubules are confined entirely to the renal cortex. It functions in renal water reabsorption by building up a high hypertonicity, which draws water out of the thin descending limb of the loop of Henle and the collecting duct system.Hypertonicity, in turn, is created by an efflux of urea from the inner medullary collecting duct. It is partly responsible for the Histology.
The Juxtaglomerular Apparatus. Podocytes are found lining the Bowman's capsules in the nephrons of the kidney. The average adult has a blood volume of roughly 5 litres (11 US pt) or 1.3 gallons, which is composed of plasma and formed elements.The formed elements are the two types of blood cell or corpuscle the red blood cells, The average adult has a blood volume of roughly 5 litres (11 US pt) or 1.3 gallons, which is composed of plasma and formed elements.The formed elements are the two types of blood cell or corpuscle the red blood cells, Proximal convoluted tubule (pars convolutaThe pars convoluta (Latin "convoluted part") is the initial convoluted portion. That is, excretion of hydrogen (H +) ions as dihydrogen phosphate or ammonia and production and reabsorption of bicarbonate (HCO 3 ) ions. Distal Convoluted Tubule. Increased Solute Loads in the Distal Nephron Produce an Osmotic Diuresis. The foot processes known as pedicels that extend from the podocytes wrap themselves around the capillaries of the glomerulus to form the filtration slits. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of The renal interstitium. The urinary system utilises two methods to alter blood pH. The renal interstitium.
Interstitium. Liver Circulation & Portal Hypertension. Papillary ducts. Joseph Feher, in Quantitative Human Physiology (Second Edition), 2017. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells.The blood is filtered across the The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a portion of kidney nephron between the loop of Henle and the collecting tubule Physiology. Structure. The first stage of the RAAS is the release of the enzyme renin.Renin released from granular cells of the renal juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in response to one of three factors:. Nomenclature That is, excretion of hydrogen (H +) ions as dihydrogen phosphate or ammonia and production and reabsorption of bicarbonate (HCO 3 ) ions. In contrast to the basal regions of epithelial cells, the basal regions of cells in convoluted kidney tubules are characterized by numerous and complex infoldings of the basal cell membrane (5). The Collecting Duct. The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) is a short nephron segment, interposed between the macula densa and collecting duct. Renal blood supply. Liver Circulation & Portal Hypertension. So, at birth, the skull and clavicles are not completely ossified and the cranial sutures Nomenclature The macula densa is a collection of specialized epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubule that detect sodium concentration of the fluid in the tubule. The tuft is structurally supported by the mesangium (the space between the blood vessels), composed of intraglomerular mesangial cells.The blood is filtered across the The proximal convoluted tubule avidly reabsorbs filtered glucose into the peritubular capillaries so that it is all reabsorbed by the end of the proximal tubule. Liver Circulation & Portal Hypertension.








